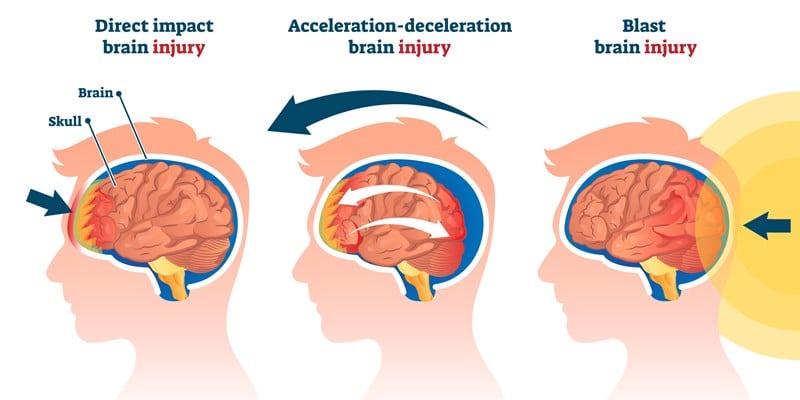
Concussions are a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow or jolt to the head or body that causes the brain to move rapidly back and forth. This sudden movement can cause the brain to bounce around or twist in the skull, creating chemical changes in your brain and sometimes stretching and damaging your brain cells. Recognising the signs of a concussion is crucial for timely treatment and recovery. But how do you know if you have a concussion? This blog post will guide you through understanding concussions, the symptoms, and when to seek medical help.
Understanding Concussions
A concussion is not just an injury for athletes or those involved in physical activities; it can happen to anyone at any age. Falls, car accidents, being struck by an object, or violent shakes to the head are common causes of concussions. It’s important to note that not all concussions result in loss of consciousness. Many people who have had a concussion never black out but may report feeling ‘dazed’ or ‘seeing stars.’
Symptoms of Concussion
The signs and symptoms of a concussion can be subtle and may not show up immediately. Symptoms can last for days, weeks, or even longer. They may include:
1. Headache or a feeling of pressure in the head
2. Temporary loss of consciousness
3. Confusion or feeling as if in a fog
4. Amnesia surrounding the traumatic event
5. Dizziness or “seeing stars”
6. Ringing in the ears
7. Nausea
8. Vomiting
9. Slurred speech
10. Delayed response to questions
11. Fatigue
Some symptoms of concussions may be immediate or delayed in onset by hours or days after injury:
1. Concentration and memory complaints
2. Irritability and other personality changes
3. Sensitivity to light and noise
4. Sleep disturbances
5. Psychological adjustment problems and depression
6. Disorders of taste and smell
Children’s Symptoms
Concussions in children can present differently than in adults. Parents should watch for these signs:
1. Appearing dazed
2. Listlessness and tiring easily
3. Irritability and crankiness
4. Loss of balance and unsteady walking
5. Excessive crying
6. Change in eating or sleeping patterns
7. Lack of interest in favourite toys or activities
When to Seek Medical Help
You should seek immediate medical attention if you or someone else has experienced a head injury, even if emergency care isn’t required. If your child has received a blow to the head that concerns you, call your child’s doctor immediately. The doctor will need to know the cause of the injury and how it occurred.
If the injured person remains conscious, is able to respond coherently and move appropriately, the injury may be mild and usually doesn’t require further testing. In this case, if you’re still concerned about symptoms, contact your doctor or other healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Recognising a concussion early on can significantly improve recovery times and reduce the risk of further complications. If you suspect that you or someone else may have a concussion, it’s essential to seek medical attention as soon as possible. Remember, every concussion injures your brain to some extent. This injury needs time and rest to heal properly. Most concussive traumatic brain injuries are mild, and people usually recover fully.
However, remember that some symptoms of a concussion can be delayed days or weeks before they appear. So even if you feel fine right after an impact, it doesn’t necessarily mean you don’t have a concussion.
It’s always better to err on the side of caution when it comes to brain health. If there’s any doubt whether someone has a concussion, it’s best to assume the person has one and take appropriate steps to ensure their safety and recovery. You can view the official UK concussion guidelines in grassroots sport If In Doubt, Sit Them Out!